| Version 9 (modified by , 10 months ago) ( diff ) |
|---|
Modifying the model code for the 'flexible' implementation variant
Implementation Guide
Contents of this page
Overview
For the flexible implementation variant of the assimilation system, one has to modify the model code so that each model task can compute several integrations of model states successively. The required extensions are described below.
Because the flexible implementation variant is more complex to implement it can be easier if one first implements the fully parallel variant and hen modifies this to obtain the code structure for the flexible variant.
External ensemble loop
Figure 1 compares the code structure of the fully parallel and flexible implementation variants. While for the fully parallel variant only the routine assimilate_pdaf has to be added in the model time stepping loop, the additional ensemble loop, a call to PDAF_get_fcst_info, and a check of the exit flag have to be added.
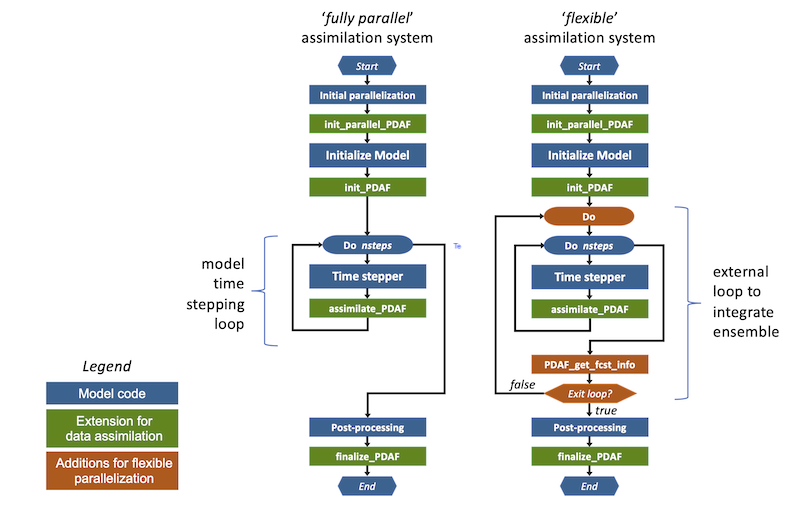
Figure 1: Comparison of the code structure for the fully parallel and flexible implementation variants. The flexible variant required more changes to the code to enable that each model task can integrate more than one ensemble state. Note that the fully parallel variant defines the number of time steps as isteps, which is the total number of steps in the program, while the flexible variant uses nsteps, which is the number of steps in one forecast phase.
In the source code, the modification can be realized in the following way:
pdaf_modelloop: DO
! PDAF: Get forecast information
CALL PDAF_get_fcst_info(nsteps, timenow, doexit)
! Check exit flag
IF (doexit==1) EXIT pdaf_modelloop
! Model time stepping loop, for example
DO i = 1, nsteps
... Time stepping code of the model ...
! Let PDAF check forecast progress and perform analysis
CALL assimilate_pdaf()
END DO
END DO pdaf_modelloop
This example is taken from the example implementation in templates/online_flexible/. The unconditional DO loop (while loop) allows for an arbirary number of repetitions. The exit of the loop is controlled by the exit flag doexit, which is obtained from PDAF_get_fcst_info. The variable nsteps, also obtained from PDAF_get_fcst_info, defines the number of time steps to be computed during the current forecast phase. This value has to be used in the model time stepping loop.
The code changes for the flexible parallelization variant can usually be obtained by adapting the code for the fully parallel implementation variant.
Apart from the changes described above we need to initialize the ensemble forecasting as in the fully parallel variant. In particular , we need to write the ensemble state vector values into the model fields. We need to set for PDAF how many time steps need to be done until the first observations are assimilated. For these operations, we call the routine PDAF_init_forecast in the routine init_pdaf. This call is identical to that used in the fully parallel' variant.
Calling PDAF_init_forecast
The call to PDAF_init_forecast is identical for the fully parallel and flexible implementation variants.
The routine is called at the end of the routine init_pdaf that was discussed on the page on initializing PDAF. The main purpose of this routine is to initialize the model fields for all model tasks from the ensemlbe of state vectors. This is done in the call-back routine distribute_state_pdaf. The routine also calls the call-back routine next_observation_pdaf to set the number of time steps for the initial forecast phase and an exit flag. These values used are internally by PDAF to control the forecast phase. Further, the routine calls the call-back-routine prepoststep_pdaf. This pre/postep routine provides the user access to the initial ensemble.
The interface of PDAF_init_forecast is:
SUBROUTINE PDAF_init_forecast(next_observation_pdaf, distribute_state_pdaf, &
prepoststep_pdaf, status)
with the arguments (where the bold names show the arguments relevant to the user for the fully-parallel variant):
- next_observation_pdaf:
The name of a user supplied routine that initializes the variablesnsteps,timenow, anddoexit - distribute_state_pdaf:
The name of a user supplied routine that initializes the model fields from the array holding the ensemble of model state vectors - prepoststep_pdaf:
The name of a user supplied routine that is called before and after the analysis step. Here the user has the possibility to access the state ensemble and can e.g. compute estimated variances or can write the ensemble states the state estimate into files. status,integer, intent(inout):
The status flag. It is zero, if the routine is exited without errors. We recommend to check the value.
The user-supplied routines are described further below.
PDAF_get_fcst_info
The interface is the following:
SUBROUTINE PDAF_get_fcst_info(nsteps, timenow, doexit)
INTEGER, INTENT(out) :: stepnow ! The current time step
INTEGER, INTENT(out) :: nsteps ! The number of time steps of the next forecast phase
INTEGER, INTENT(out) :: doexit ! Exit flag: (1) exit, (0) continue data assimilation
These variables are intialized by next_observation_pdaf that was called by PDAF_init_forecast. At later forecast phases in the assimilation processing, the analysis routine PDAF3_assimilation (or more specifalize routines) will case next_observation_pdaf.
Inserting assimilate_pdaf into the model code
The right place to insert the routine assimilate_pdaf into the model code is the same as for the fully parallel implementation variant. Usually this is at the end of the model time stepping loop, thus when the model completed the computation of a single time step. In most cases, this is just before the 'END DO' in the model source code. However, there might be special cases, where the model does some additional operations so that the call to assimilate_pdaf should be insered somewhat earlier.
Using assimilate_pdaf
The purpose of assimilate_pdaf is to call the universal PDAF-core routine PDAF3_assimilate (or a more specific varant of this routine). The arguments of PDAF3_assimilate are mainly the names of user-supplied call-back routines, except from an argument for the status flag. These names are specified in assimilate_pdaf as 'external'.
The routine assimilate_pdaf is called at each time step of the model forecast. This allows to, e.g., apply incremental analysis updates.
Details on the implementations of the user-routines for the analysis step ar provided in the Page on implementating the analysis step.
User-supplied routines
Here, we discuss the user-supplied routines that are arguments of PDAF_init_forecast.
In the section titles below we provide the name of the template file in parentheses.
next_observation_pdaf (next_observation_pdaf.F90)
The interface is:
SUBROUTINE next_observation_pdaf(stepnow, nsteps, doexit, timenow) INTEGER, INTENT(in) :: stepnow ! The current time step provided by PDAF INTEGER, INTENT(out) :: nsteps ! The number of time steps of the next forecast phase INTEGER, INTENT(out) :: doexit ! Exit flag: (1) exit, (0) continue data assimilation REAL, INTENT(out) :: timenow ! Current (physical) model (physical) time. Not used by PDAF itself.
The routine is called by PDAF_init_forecast and later at the beginning of each forecast phase by PDAF3_assimilate, or similar routines. It is executed by all processes that participate in the model integrations.
Based on the information of the current time step, the routine has to define the number of time steps nsteps for the next forecast phase and the exit flag doexit. In the user code, one accesses these variables with PDAF_get_fcst_info as explained above.
Some hints:
- We assume that the time interval between successive observations is known. Then,
nstepscan be simply initialized by dividing the time interval by the size of the time step. - It is up to the user to define
timenowbecause it is only used in the user-code. The user can either ignore it (setting to to 0.0), or could use it freely to indicate the model time. At the first call tonext_observation_pdafthe variabletimenowcan be initialized with the current model time. At the next call a forecast phase has been completed. Thus, the new value oftimenowfollows from the timer interval for the previous forecast phase and can be incremented accordingly. In the user code, one can accesstimenowwith a call to PDAF_get_fcst_info. - Inside PDAF,
doexitis used as follows: Ifnsteps=0ordoexit=1is set, the ensemble state will not be distributed by PDAF (thusdistribute_state, see below, is not called). If one intends to proceed with ensemble forecasting, one has to setnstepsto a value >0 anddoexit=0. - The total number of time steps set for the assimilation experiment (variable
istepsin Fig. 1) defines when the model integrations end. Ifnstepsis set so that it specifies a time step larger thanistepsnot all of these steps will be computed.
distribute_state_pdaf (distribute_state_pdaf.F90)
The interface for this routine is
SUBROUTINE distribute_state(dim_p, state_p) INTEGER, INTENT(in) :: dim_p ! Size of state vector for process-local sub-domain REAL, INTENT(inout) :: state_p(dim_p) ! State vector for process-local sub-domain
The routine is called by PDAF_init_forecast and later at the beginning of each forecast phase by PDAF3_assimilate, or similar routines. It is executed by all processes that participate in the model integrations.
PDAF calls this routine providing the state vector state_p and its size dim_p. The routine has to write the information from the state vector into the model field arrays.
Some hints:
- The user has defined the setup of the state vector, so that it is know which model fields are stored at which position in the state vector and in which order, for example, a 3-dimensional model field is stored. This was already used in
init_ens_pdaf. - The code usually consist of (nested) loops through each of the model fields, one field at a time. In the loop each element of the state vector is written into an element of a model field array.
- If the model is not parallelized,
state_pwill contain a full state vector. If the model is parallelized using domain decomposition,state_pwill contain the part of the state vector that corresponds to the model sub-domain for the calling process.
prepoststep_pdaf (prepoststep_ens_pdaf.F90)
The interface for this routine is
SUBROUTINE prepoststep(step, dim_p, dim_ens, dim_ens_p, dim_obs_p, &
state_p, Ainv, ens_p, flag)
INTEGER, INTENT(in) :: step ! Current time step
! (When the routine is called before the analysis -step is provided.)
INTEGER, INTENT(in) :: dim_p ! Process-local state dimension
INTEGER, INTENT(in) :: dim_ens ! Size of state ensemble
INTEGER, INTENT(in) :: dim_ens_p ! Process-local ensemble size (not relevant for fully parallel)
INTEGER, INTENT(in) :: dim_obs_p ! Process-local dimension of observation vector
REAL, INTENT(inout) :: state_p(dim_p) ! Process-local state vector
! The array 'state_p' is not generally not initialized.
! It can be used freely in this routine.
REAL, INTENT(inout) :: Ainv(dim_ens-1, dim_ens-1) ! Inverse of matrix A )only for special cases)
REAL, INTENT(inout) :: ens_p(dim_p, dim_ens) ! State ensemble for process-local sub-domain
INTEGER, INTENT(in) :: flag ! PDAF status flag
The routine prepoststep_pdaf is called once at the beginning of the assimilation process. In addition, it is called during the assimilation cycles before the analysis step and after the ensemble transformation. The routine is called by all filter processes (that is filterpe=.true.).
With this routine, PDAF provides the user the full access to the ensemble of model states. Thus, user-controlled pre- and post-step operations can be performed. For example the forecast and the analysis states and ensemble covariance matrix can be analyzed, e.g. by computing the estimated variances. If the smoother is used, also the smoothed ensembles can be analyzed. In addition, the estimates can be written to disk.
The routine also allows to perform adjustments to the state vectors, e.g. for balances, in the ensemble.
Hints:
- The state vector,
state_p, is usually not initialized because the ensemble DA methods focus on computing the ensemble and not its mean state. Thus the user would need to compute the ensemble mean, if this is required. This array can be used freely inprepoststep_pdaf. - The interface of
prepoststep_pdafdoes not include the array of smoothed ensembles. In order to access the smoother ensemble array, one has to set a pointer to it using a call to the routinePDAF_get_smootherens(see page on auxiliary routines).
Compiling and testing
To be able to test the ensemble forecasting, we need also need the user-supplied routine collect_state_pdaf. This routine writes the model fields after a forecast into the state vectors. This will be done in the call to PDAF3_assimilate in assimilate_pdaf. While we explain assimilate_pdaf on the following page, we include collect_state_pdaf here.
Having implemented also collect_state_pdaf, one can test the program without having implemented the actual assimilation step. In the template code template/online all required user-supplied routines are included, but they don't contain functionality. However, one can use them to be able to compile and run the assimilation program for testing. In particular one can check if the ensemble forecasting works correctly.
collect_state_pdaf (collect_state_pdaf.F90)
The interface for this routine is
SUBROUTINE collect_state(dim_p, state_p) INTEGER, INTENT(in) :: dim_p ! State dimension for process-local model sub-domain REAL, INTENT(inout) :: state_p(dim_p) ! State vector for process-local model sub-domain
This routine is called during the forecast phase as many times as there are states to be integrated by a model task. It is called at the end of the integration of a state from the ensemble. The routine is executed by all processes that belong to model tasks.
When the routine is called, a state vector state_p and its size dim_p are provided. The operation to be performed in this routine is inverse to that of the routine distribute_state_pdaf. That is, the state vector state_p has to be filled from the model fields.
Hint:
- If the model is not parallelized,
state_pwill contain a full state vector. If the model is parallelized using domain decomposition,state_pwill contain the part of the state vector that corresponds to the model sub-domain for the calling process.
