Implementation Concept of the Offline Mode
Offline mode: Separating model integrations and assimilation step
Implementation Concept
- General Concept
- Online Mode
- Offline Mode
Contents of this page
The offline mode of PDAF separates the model forecasts from the analysis step of the data assimialtion. The ensemble integrations are performed by the numerical model. After all ensemble members are integrated to the time when observations are to be assimilated, the assimilation program containing PDAF is started. This program reads the files from the model for all ensemble members. Subsequently, the analysis step of the chosen filter algorithm is computed. Finally, the updated ensemble states are written into input or restart files of the model. This completes the analysis step such that the next forecast phase can be computed.
In the forecast phase, the user has to run the numerical model seprately for each ensemble member state. Each model forecast has to be initialized by the state fields of the ensemble member. At the end of each single forecast integration, the model writes the forecast fields into regular output or restart files. Within the offline mode of PDAF, we leave it to the user to control the model runs. As these are regular model integrations, it should be easiest to use the regular scripts used also to perform a free model integration without data assimilation. However, the user has to take care that the output files from each ensemble member are stored separately.
The assimilation program is a simplified implementation of what is required when PDAF is used in its online mode. In particular, no explicit linkage to the model code and no forecast phase are required. Essentially, one just needs a driver program that calls the PDAF routines. The general structure of the program for the offline assimilation program is depicted on the right hand side of Figure 1.
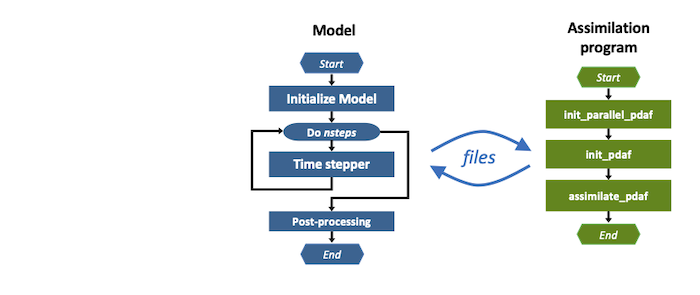
Figure 1: The offline mode exchanges information on model fields and the model grid information using disk files. For the assimilaton program the typical structure is shown.
The structure of the assimilation program is the following:
- init_parallel_pdaf: This routine is executed at the beginning of the program. This subroutine creates the parallel environment for PDAF. In the offline mode, it is possible to execute the assimilation program on a single processor, even if the model is parallelized. With local filter methods, one can also use OpenMP (shared memory) parallelization. The routine calls the PDAF core routine
PDAF3_set_parallelto provide the parallelization variables to PDAF (in implementations of PDAF before verison 3.0, this call is not present). - init_pdaf: The routine
init_pdafis executed next. In this routine, parameters for PDAF can be defined and then the core initialization routinePDAF3_initis called (in implementations of PDAF before version 3.0, this routine was calledPDAF_init). This core routine initializes internal parameters and afterwards the array of ensemble states using a user-provided call-back routine. In case of the offline mode, this means that the ensemble is read from the output files of the model. - assimilation_pdaf: This routine executes the analysis step. It declares the names of user-supplied subroutines and then the PDAF core routine
PDAF3_assim_offlinefor the assimilation is executed (With PDAF before version 3.0, a routinePDAFomi_put_state_Xis used, where X is replaced by the specific type of DA method, e.g. X=local). For the offline mode there is no ensemble integration in the assimilation program. Thus, this subroutine directly computes the analysis step. In a user-supplied subroutine called byPDAF3_assim_offline, the ensemble of analysis states is finally written into restart files for the next forecast phase performed by model integrations initialized from these files. - finalize_PDAF: This routine is used to let PDAF display timing and memory information and to call PDAF to deallocate its internal arrays.
A code example for the offline mode is provided in the tutorial code in tutorial/offline_2D_serial. See also the PDAF implementation tutorial, which explains the code structure and implementation steps on the basis of the tutorial code. A more abstract description of the implementation is provided by the Offline Implementation Guide.
|
Important aspects of the implementation concept
- With the offline mode of PDAF, no direct coupling between PDAF and the model code is required. The exchange of information between the model and the assimilation program is performed solely through the output and restart files of the model. It requires that the user implements routines to read the model fields from the forecast files and routines that write the analysis state ensemble into restart files of the model.
- PDAF uses the concept to 'pull' information at the time when it is needed. Model-specific operations like reading the model files and initializing the array of ensemble states in
PDAF_initare performed by user-supplied subroutines, which are executed by PDAF as call-back routines. Also the reading of observational infromation is performed by user-supplied call-back subroutines.
These can be implemented in the users programming style and just have to be consistent with the interface. Details on the interface and the required routines are given on the pages describing the implementation steps. The concept of the call-back routines is depicted in Fig. 2.
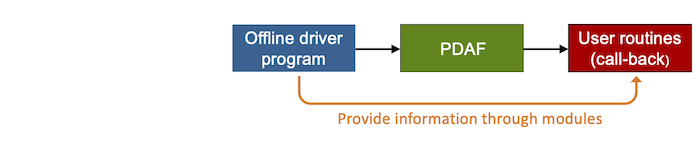
Figure 2: The assimilation program consist of the driver program, the PDAF core, and user-supplied call-back routines.
- With regard to the parallelization, the assimilation program can be run on a single processor. The variables for the parallelization still have to be initialized by calling
init_parallel_pdaf. - For large-scale models, it can be useful to execute the assimilation program with parallelization. The easiest approach is to use the OpenMP-parallelization of the local ensemble filter algorithms in PDAF. One can also explicitly decompose the state vector. An easy strategy for this can be to follow the domain decomposition of the model. In this case the decomposition information from the model has to be read into the assimilation program in order to initialize the state dimension of the sub-domains as well as the coordinates for each sub-domain.
- The core routines of PDAF (those with the prefix
PDAF_) are identical for the online and offline modes.
